Multi-level Pipeline
Overview
Runtime scheduling for an operator mainly includes the operations InferShape (including updating the shape), Resize (including tiling calculation and updating the memory size) and Launch (including memory request and release), which can only be sent to the device (NPU/GPU) after the host completes these operations. When the host processing speed can not keep up with the operator's device execution time, the device side will produce bubbles, resulting in the device arithmetic can not be maximized to use, affecting the overall performance. For this reason, MindSpore proposed a multi-stage runtime streaming issued to take full advantage of the resources of the host multi-threaded. These operations of host are disassembled into separate operation units and issued in a stream, which greatly improves the efficiency of host issuance.

Basic Principle
Multi-stage flow is a key performance optimization point for runtime, which improves runtime scheduling efficiency by task decomposition and parallel flow issued to give full play to CPU multi-core performance. The main flow is as follows:
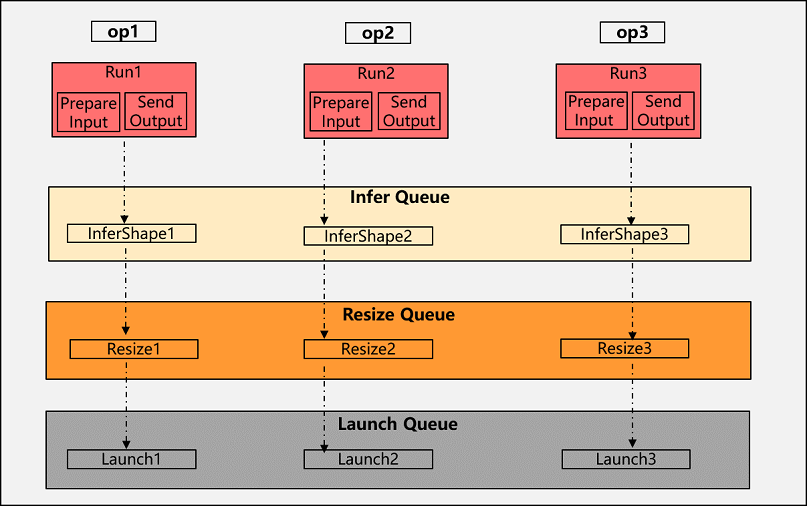
Task decomposition: the operator scheduling is decomposed into three tasks InferShape, Resize and Launch.
Queue creation: Create three queues, Infer Queue, Resize Queue and Launch Queue, for taking over the three tasks in step 1.
Streaming scheduling: after the first operator collects the input, it only needs to send the InferShape task down to the Infer queue, so that the output data of the operator can be sent to the next operator. After InferShape is completed, the Resize task of the operator will be sent down to the Resize queue, and finally, after Resize is completed, the LaunchKernel task is sent to the Launch queue.