量子启发式算法NPU后端使用教程
本篇教程基于MindQuantum介绍量子启发式算法的NPU后端的参数细节和使用方法,并提供实战教程,带领开发者手把手入门。
本文将从下面六点进行展开说明:
昇腾平台介绍,NPU芯片的特点性能。
系统环境配置,检查硬件并安装软件。
介绍MindQuantum和量子启发式算法。
介绍量子启发式算法NPU后端支持的精度类型,提供矩阵运算样例代码。
使用量子启发式算法NPU后端求解最大割问题。
对比量子启发式算法在CPU和NPU后端上的性能优势。
昇腾平台介绍
达芬奇NPU核心:专为矩阵运算优化的3D Cube架构,昇腾芯片提供256TOPS INT8算力。
混合精度计算:支持FP32/FP16/INT8混合精度,满足深度学习、大模型训练推理和量子计算不同阶段计算需求。
超高能效比:相比传统GPU能效提升2-3倍,降低运营成本。
系统环境配置
硬件配置
支持昇腾NPU
支持算子版本:CANN-7/CANN-8
[1]:
# 配置环境变量
!source /usr/local/Ascend/ascend-toolkit/set_env.sh
[2]:
import os
os.environ["LD_LIBRARY_PATH"] = ":".join(
[
"/usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64:",
"/usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64/common:",
"/usr/local/Ascend/ascend-toolkit/latest/aarch64-linux/lib64:",
"/usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64/driver:",
os.environ.get("LD_LIBRARY_PATH", ""),
]
)
[3]:
# 输出系统NPU型号、数量、驱动版本
!npu-smi info
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| npu-smi 23.0.3 Version: 23.0.3 |
+---------------------------+---------------+----------------------------------------------------+
| NPU Name | Health | Power(W) Temp(C) Hugepages-Usage(page)|
| Chip | Bus-Id | AICore(%) Memory-Usage(MB) HBM-Usage(MB) |
+===========================+===============+====================================================+
| 0 910 | OK | 93.8 40 0 / 0 |
| 0 | 0000:C1:00.0 | 0 0 / 0 3326 / 65536 |
+===========================+===============+====================================================+
+---------------------------+---------------+----------------------------------------------------+
| NPU Chip | Process id | Process name | Process memory(MB) |
+===========================+===============+====================================================+
| No running processes found in NPU 0 |
+===========================+===============+====================================================+
软件安装
[4]:
# 可选,已安装软件则不需要执行此步
# !pip install torch_npu
# !pip install mindquantum
验证NPU是否正常可用
[5]:
# 检查NPU是否可用
import torch_npu
torch_npu.npu.is_available()
[5]:
True
MindQuantum介绍
MindQuantum是基于昇思MindSpore开源深度学习平台开发的新一代通用量子计算框架,聚焦于NISQ阶段的算法实现与落地。结合HiQ高性能量子计算模拟器和昇思MindSpore并行自动微分能力,提供极简的开发模式和极致的性能体验。
MindQuantum已经集成量子启发式算法模块,并提供CPU、GPU、NUP/昇腾版本,适配多种硬件设备,并提供极致性能。
量子启发式算法是一类基于量子力学原理的计算方法衍生或启发的经典力学方法,旨在利用量子力学的独特性质(叠加态、量子纠缠和量子并行性)来改进传统算法的性能。
常见的量子启发式算法包括:
ASB(Adiabatic Simulated bifurcation/绝热模拟分叉算法)
BSB(Ballistic Simulated bifurcation/弹道模拟分叉算法)
DSB(Discrete Simulated bifurcation/离散模拟分叉算法)
SimCIM(Simulated Coherent Ising Machine/模拟相干伊辛机算法)
LQA(Local Quantum Annealing/局部量子退火算法)
量子启发式算法NPU后端
量子启发式算法支持后端:
backend (str) - 计算后端和精度:‘cpu-float32’、‘gpu-float32’、‘gpu-float16’、‘gpu-int8’ 或 ‘npu-float32’,默认值: ‘cpu-float32’。
NPU后端现支持的数据精度:float32
矩阵运算样例
[6]:
from scipy.sparse import coo_matrix
from mindquantum.algorithm.qaia import DSB
# 矩阵[[0,-1],[-1,0]]
J = coo_matrix(([-1, -1], ([0, 1], [1, 0])), shape=(2, 2))
solver = DSB(J, batch_size=10, backend="npu-float32")
solver.update()
cut = solver.calc_cut()
energy = solver.calc_energy()
print(f"Cut: {cut}\nEnergy: {energy}")
Warning: Device do not support double dtype now, dtype cast repalce with float.
Cut: tensor([0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 0.], device='npu:0')
Energy: tensor([ 1., -1., -1., -1., -1., -1., 1., -1., -1., 1.], device='npu:0')
实战案例-使用量子启发式算法求解最大割问题
[7]:
# 导入需要的Python模块
from mindquantum.algorithm.qaia import DSB
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from scipy.sparse import coo_matrix
import time
[8]:
# 数据准备
# 下载数据,无向图数据集来源于GSet
import requests
graph_file = "https://web.stanford.edu/~yyye/yyye/Gset/G22"
# 使用requests库中的get方法发送HTTP请求,将url的响应结果存入变量,再以二进制写入模式打开文件写入本地
response = requests.get(graph_file)
open("G22", "wb").write(response.content)
# 如果上述-下载图集的代码执行,报错TimeoutError,说明是网络问题
# 可以手动点击网址 https://web.stanford.edu/~yyye/yyye/Gset/G22,下载数据,保存在本地,与该教程同级目录
[8]:
217828
[9]:
# 数据处理
def read_gset(filename, negate=True):
# 读取图表
graph = pd.read_csv(filename, sep=" ")
# 节点的数量
n_v = int(graph.columns[0])
# 边的数量
n_e = int(graph.columns[1])
# 如果节点和边不匹配,会抛出错误
assert n_e == graph.shape[0], "The number of edges is not matched"
# 将读取的数据转换为一个COO矩阵(Coordinate List Format),并返回一个稀疏矩阵
G = coo_matrix(
(
np.concatenate([graph.iloc[:, -1], graph.iloc[:, -1]]),
(
np.concatenate([graph.iloc[:, 0] - 1, graph.iloc[:, 1] - 1]),
np.concatenate([graph.iloc[:, 1] - 1, graph.iloc[:, 0] - 1]),
),
),
shape=(n_v, n_v),
)
if negate:
G = -G
return G
G = read_gset("./G22")
[10]:
start_time = time.time()
solver = DSB(G, batch_size=100, n_iter=1000, backend="npu-float32")
solver.update()
cut = solver.calc_cut()
end_time = time.time()
print(f"G22 MAXCut is : {max(cut)}\nuse time:{end_time-start_time}")
G22 MAXCut is : 13353.0
use time:0.5273990631103516
性能对比
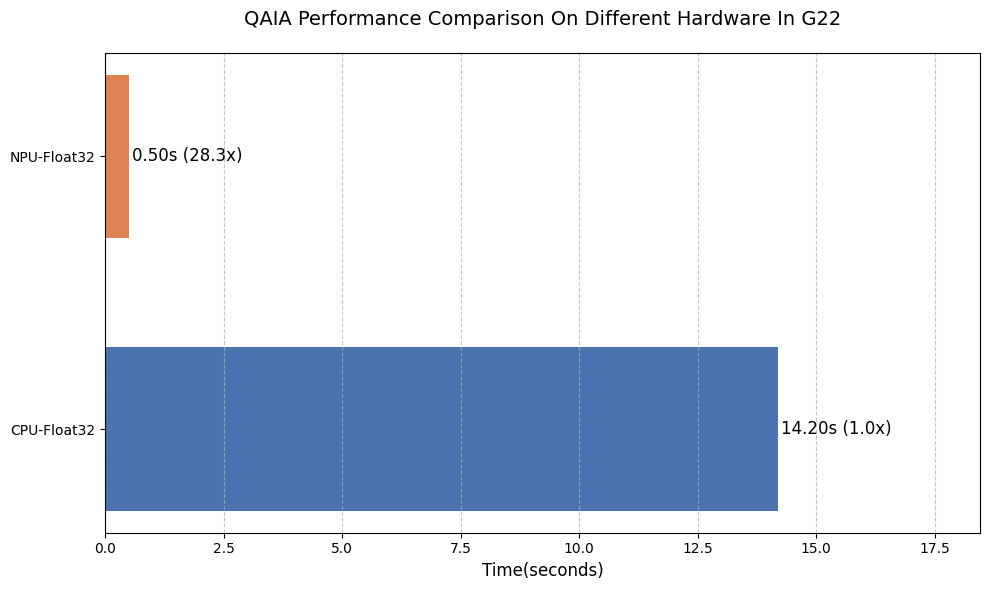
对比BSB算法在CPU和NPU后端上求解最大割问题的性能优势
[11]:
import time
start_time = time.time()
solver = DSB(G, batch_size=100, n_iter=1000, backend="cpu-float32")
solver.update()
cut = solver.calc_cut()
cpu_fp32_time = time.time() - start_time
start_time = time.time()
solver = DSB(G, batch_size=100, n_iter=1000, backend="npu-float32")
solver.update()
cut = solver.calc_cut()
npu_fp32_time = time.time() - start_time
[12]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 计算加速比
cpu_speedup = cpu_fp32_time / cpu_fp32_time
npu_speedup = cpu_fp32_time / npu_fp32_time
devices = ["CPU-Float32", "NPU-Float32"]
times = [cpu_fp32_time, npu_fp32_time]
speedups = [cpu_speedup, npu_speedup]
colors = ["#4C72B0", "#DD8452"]
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6), dpi=100)
# 绘制横向条形图, 表示不同后端的计算时间
bars = plt.barh(devices, times, color=colors, height=0.6)
# 添加数据标签和加速比
for i, (time, speedup) in enumerate(zip(times, speedups)):
plt.text(
time + 0.05,
i,
f"{time:.2f}s ({speedup:.1f}x)",
va="center",
fontsize=12,
)
plt.title(
"QAIA Performance Comparison On Different Hardware In G22", fontsize=14, pad=20
)
plt.xlabel("Time(seconds)", fontsize=12)
plt.xlim(0, max(times) * 1.3)
plt.grid(axis="x", linestyle="--", alpha=0.7)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
[13]:
from mindquantum.utils.show_info import InfoTable
InfoTable("mindquantum", "scipy", "numpy")
[13]:
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| mindquantum | 0.11.0 |
| scipy | 1.11.3 |
| numpy | 1.26.1 |
| System | Info |
| Python | 3.9.18 |
| OS | Linux aarch64 |
| Memory | 1622.53 GB |
| CPU Max Thread | 192 |
| Date | Thu Sep 4 20:11:56 2025 |