Perform Inference on Mini and Small Systems
Linux IoT C++ codegen Beginner Intermediate
Overview
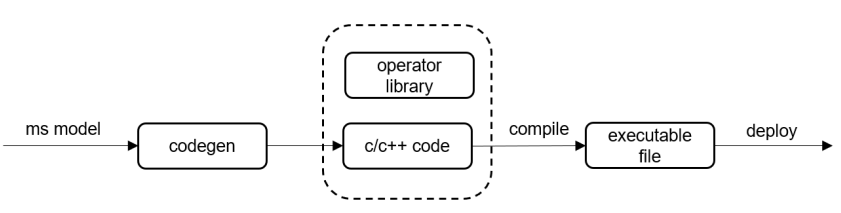
MindSpore Lite provides a code generator tool, namely codegen, which could have runtime compiling and computational graphs building done offline. Only necessary codes and information are kept in the generated program, thereby minimizing the size of the generated inference program. codegen supports operators in NNACL and CMSIS, and generates inference programs running on x86/ARM64/ARM32A/ARM32M platforms.
Here is the process of using codegen:
Use the MindSpore Lite Converter to convert the pre-trained model into a
*.msfile.Use codegen and input the
*.msfile to automatically generate the inference code.
Obtaining codegen
You can obtain codegen by any of the following ways:
Download pre-compiled Release Package from MindSpore.
Build from the source.
Currently the code generator is only available on Linux x86_64.
Directory Structure
mindspore-lite-{version}-linux-x64
└── tools
└── codegen # Code generation tool
├── codegen # Executable program
├── include # Header files of inference framework
│ ├── nnacl # nnacl operator header file
│ └── wrapper
├── lib
│ └── libwrapper.a # MindSpore Lite codegen generates code dependent operator static library
└── third_party
├── include
│ └── CMSIS # ARM CMSIS NN operator header files
└── lib
└── libcmsis_nn.a # ARM CMSIS NN operator static library
Parameter Description
Here is the detailed description of parameters:
Parameter |
Mandatory or Not |
Parameter Description |
Value Range |
Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
help |
No |
print help information |
- |
- |
codePath |
Yes |
path of the generated code |
- |
./(current dir) |
target |
Yes |
target platform for the generated code |
x86, ARM32M, ARM32A, ARM64 |
x86 |
modelPath |
Yes |
the path to the input model |
- |
- |
supportParallel |
No |
generate parallel codes or not |
true, false |
false |
debugMode |
No |
generate debug codes or not |
true, false |
false |
The input model should be converted into .ms file using MindSpore Lite Converter.
debugMode is not available when the filesystem is not supported.
Please check the API Document to get the detailed API description.
The following 3 interfaces are currently not supported:
virtual std::unordered_map<String, mindspore::tensor::MSTensor *> GetOutputs() const = 0;
virtual Vector<tensor::MSTensor *> GetOutputsByNodeName(const String &node_name) const = 0;
virtual int Resize(const Vector<tensor::MSTensor *> &inputs, const Vector<Vector<int>> &dims) = 0;
Running codegen
The example starts with a pre-trained classification model for the MNIST dataset.
./codegen --modelPath=./mnist.ms --codePath=./
After successful execution, codegen would generate a folder named mnist at the specified path. The structure of the project file is shown as follows:
mnist
├── benchmark # Benchmark model for debugging
│ ├── benchmark.cc
│ ├── calib_output.cc
│ ├── calib_output.h
│ ├── load_input.c
│ └── load_input.h
├── CMakeLists.txt
└── src # source files
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── mmodel.h
├── net.bin # binary model weights
├── net.c
├── net.cmake
├── net.h
├── session.cc
├── session.h
├── tensor.cc
├── tensor.h
├── weight.c
└── weight.h
Performing Inference on STM Boards
This guide takes the deployment on STM32F746 as an example to show how the pre-complied model is built and deployed on Cortex-M platform. More information about Arm Cortex-M could be found in their Official Web Site.
STM32F746 Compile Dependencies
The generated program compilation and deployment need to install the following tools on Windows: J-Link, STM32CubeMX and GNU Arm Embedded Toolchain to perform Cross-compilation.
STM32CubeMX Windows Version >= 6.0.1
GNU Arm Embedded Toolchain >= 9-2019-q4-major-win32
J-Link Windows Version >= 6.56
GCC >= 7.3.0
CMake >= 3.18.3
STM32F746 Project Construction
The structure of the project files that needs to be managed as follows:
├── mnist # generated inference code by codegen ├── include # API header files (needs to be managed) └── operator_library # operator source code (needs to be managed)
API header files could be found in the Release Package provided by the MindSpore team.
You need to obtain the source code corresponding to the target platform because the pre-compiled static library is not provided since the Cross compilation on Cortex-M platform is complicated. The corresponding project file structure is provided in the example and you could follow the instructions shown below to copy the source code and finish the compilation.
Use codegen to compile MNIST handwriting number identification model, generate corresponding inference codes for STM32F46. The command is as follows:
./codegen --codePath=. --modelPath=mnist.ms --target=ARM32M
The generated project file structure is shown below:
├── mnist # root of the generated code ├── benchmark # generated benchmark code └── src # generated model inference codeThe file structure of the prepared static operator library is shown below:
├── operator_library # operator library ├── include # header files of operator library └── nnacl # operator source code provided by MindSpore team └── wrapper # operator source code provided by MindSpore team └── CMSIS # CMSIS source code provided by Armarm_nnfunctions.hneeds to be added when using CMSIS v5.7.0 Softmax operator.
Project Compiling
Environment testing
When programs needed for Cross-compilation are installed, add them to the Windows PATH one by one, and test them with the following instructions:
gcc -v # Check GCC arm-none-eabi-gdb -v # Check Cross compiler jlink -v # Check J-Link make -v # Check Make
If all success, the environment preparation is done.
Generate the initialization codes run on the STM32F746 board. (detailed code example)
start STM32CubeMX, new project and choose STM32F746IG.
Choose
Makefileandgenerator code.Launch
cmdon the generated project root, executemaketo test whether the initialization code compilation is successful.
# make success result arm-none-eabi-size build/test_stm32f746.elf text data bss dec hex filename 3660 20 1572 5252 1484 build/test_stm32f746.elf arm-none-eabi-objcopy -O ihex build/test_stm32f746.elf build/test_stm32f746.hex arm-none-eabi-objcopy -O binary -S build/test_stm32f746.elf build/test_stm32f746.bin
Compiling Model
Copy operator library source code and header files provided by MindSpore team to the project folder generated by STM32CubeMX.
Copy model inference code generated by codegen to the project folder generated by STM32CubeMX.
├── .mxproject ├── build # compile output folder ├── Core ├── Drivers ├── mnist # cortex-m7 model inference code generated by codegen ├── Makefile # modify makefile to organize mnist && operator_library source code ├── startup_stm32f746xx.s ├── STM32F746IGKx_FLASH.ld └── test_stm32f746.ioc
Modify makefile, organize operator library source code and generated inference code, check example to get detailed information about makefile.
# C includes C_INCLUDES = \ -ICore/Inc \ -IDrivers/STM32F7xx_HAL_Driver/Inc \ -IDrivers/STM32F7xx_HAL_Driver/Inc/Legacy \ -IDrivers/CMSIS/Device/ST/STM32F7xx/Include \ -Imnist/operator_library/include \ # Added, header files for operator library -Imnist/include \ # Added, header files of model inference code -Imnist/src # Added, source code of model inference code ......
Add code in
Core/Src/main.cto call inference API. The code to be added is shown below:while (1) { /* USER CODE END WHILE */ SEGGER_RTT_printf(0, "***********mnist test start***********\n"); const char *model_buffer = nullptr; int model_size = 0; session::LiteSession *session = mindspore::session::LiteSession::CreateSession(model_buffer, model_size, nullptr); Vector<tensor::MSTensor *> inputs = session->GetInputs(); size_t inputs_num = inputs.size(); void *inputs_binbuf[inputs_num]; int inputs_size[inputs_num]; for (size_t i = 0; i < inputs_num; ++i) { inputs_size[i] = inputs[i]->Size(); } // here mnist only have one input data,just hard code to it's array; inputs_binbuf[0] = mnist_inputs_data; for (size_t i = 0; i < inputs_num; ++i) { void *input_data = inputs[i]->MutableData(); memcpy(input_data, inputs_binbuf[i], inputs_size[i]); } int ret = session->RunGraph(); if (ret != lite::RET_OK) { return lite::RET_ERROR; } Vector<String> outputs_name = session->GetOutputTensorNames(); for (int i = 0; i < outputs_name.size(); ++i) { tensor::MSTensor *output_tensor = session->GetOutputByTensorName(outputs_name[i]); if (output_tensor == nullptr) { return -1; } float *casted_data = static_cast<float *>(output_tensor->MutableData()); if (casted_data == nullptr) { return -1; } for (size_t j = 0; j < 10 && j < output_tensor->ElementsNum(); j++) { SEGGER_RTT_printf(0, "output: [%d] is : [%d]/100\n", i, casted_data[i] * 100); } } delete session; SEGGER_RTT_printf(0, "***********mnist test end***********\n");
Launch
cmdas admin and runmaketo compile.make
STM32F746 Project Deployment
Deploy executable files to the board using J-Link and perform inference.
jlinkgdbserver # start jlinkgdbserver set target device as STM32F746IG
jlinkRTTViewer # start jlinkRTTViewer set target devices as STM32F746IG
arm-none-eabi-gdb # start arm-gcc gdb service
file build/target.elf # open debugging file
target remote 127.0.0.1 # connect jlink server
monitor reset # reset board
monitor halt # halt board
load # load executable to board
c # perform model inference
Performing Inference on HarmonyOS Lite
Installing build environment
For the environment preparation, please refer to HarmonyOS quick start, including gn/ninja/llvm.
Connecting to the board
For Hardware environment preparation, please refer to the HarmonyOS quick start How to Develop of board Hi3516 as example.
Compiling the model
Compile mnist.ms model for HarmonyOS lite using codegen:
./codegen --modelPath=./mnist.ms --codePath=./ --target=ARM32A
Writing build scripts
For the HarmonyOS application development, please refer to demo. Copy the mnist directory generated in the previous step to any HarmonyOS source code path, assuming it is applications/sample/, and then create a new BUILD.gn file
<harmony-source-path>/applications/sample/mnist
├── benchmark
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── BUILD.gn
└── src
Download the precompile runtime component for openharmony in Download page. This is a BUILD.gn example:
import("//build/lite/config/component/lite_component.gni")
import("//build/lite/ndk/ndk.gni")
lite_component("mnist_benchmark") {
target_type = "executable"
sources = [
"benchmark/benchmark.cc",
"benchmark/calib_output.cc",
"benchmark/load_input.c",
"src/net.c",
"src/weight.c",
"src/session.cc",
"src/tensor.cc",
]
features = []
include_dirs = [
"<YOUR MINDSPORE LITE RUNTIME PATH>/runtime",
"<YOUR MINDSPORE LITE RUNTIME PATH>/tools/codegen/include",
"//applications/sample/mnist/benchmark",
"//applications/sample/mnist/src",
]
ldflags = [
"-fno-strict-aliasing",
"-Wall",
"-pedantic",
"-std=gnu99",
]
libs = [
"<YOUR MINDSPORE LITE RUNTIME PATH>/runtime/lib/libmindspore-lite.a",
"<YOUR MINDSPORE LITE RUNTIME PATH>/tools/codegen/lib/libwrapper.a",
]
defines = [
"NOT_USE_STL",
"ENABLE_NEON",
"ENABLE_ARM",
"ENABLE_ARM32"
]
cflags = [
"-fno-strict-aliasing",
"-Wall",
"-pedantic",
"-std=gnu99",
]
cflags_cc = [
"-fno-strict-aliasing",
"-Wall",
"-pedantic",
"-std=c++17",
]
}
<YOUR MINDSPORE LITE RUNTIME PATH> is the path where the runtime was unzipped, e.g. “//applications/sample/mnist/mindspore-lite-1.3.0-ohos-aarch32”.
Add the configuration of the mnist_benchmark component to the build/lite/components/applications.json file.
{
"component": "mnist_benchmark",
"description": "Communication related samples.",
"optional": "true",
"dirs": [
"applications/sample/mnist"
],
"targets": [
"//applications/sample/mnist:mnist_benchmark"
],
"rom": "",
"ram": "",
"output": [],
"adapted_kernel": [ "liteos_a" ],
"features": [],
"deps": {
"components": [],
"third_party": []
}
},
Add the configuration of the mnist_benchmark component to the vendor/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/config.json.
{ "component": "mnist_benchmark", "features":[] }
Building benchmark
cd <OPENHARMONY SOURCE PATH>
hb set
.
(select ipcamera_hispark_taurus@hisilicon)
hb build mnist_benchmark
The result file is generated in out/hispark_taurus/ipcamera_hispark_taurus directory.
Running benchmark
Copy mnist_benchmark, net.bin and mnist_input.bin to the board, and run:
OHOS # ./mnist_benchmark mnist_input.bin net.bin 1
OHOS # =======run benchmark======
input 0: mnist_input.bin
loop count: 1
total time: 10.11800ms, per time: 10.11800ms
outputs:
name: int8toft32_Softmax-7_post0/output-0, DataType: 43, Elements: 10, Shape: [1 10 ], Data:
0.000000, 0.000000, 0.003906, 0.000000, 0.000000, 0.992188, 0.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000,
========run success=======
Register Kernel
Currently, Users can only register their own kernels for custom operator. We will support registering the built-in operators’ kernels in the future. We use Hi3516D board as an example to show you how to use kernel register in codegen.
Prepare the model file
You need to get a ms model that contains custom operators. Please refer to Usage Description of the Integrated NNIE.
Run codegen
Codegen can generate custom kernel’s function declaration and reference code if the model has custom operators. Generate source codes for a model named nnie.ms:
./codegen --modelPath=./nnie.ms --target=ARM32A
Implement custom kernel by users
A header file named registered_kernel.h in the generated files. The custom kernel function is declared in this file:
int CustomKernel(TensorC *inputs, int input_num, TensorC *outputs, int output_num, CustomParameter *param);
Users need to implement this function then add their source files to the cmake project. For example, we provide a sample library named libmicro_nnie.so in the nnie runtime package, download. The library contains the implementation of custom kernel for NNIE. Users can download it and modify the CMakeLists.txt:
link_directories(<YOUR_PATH>/mindspore-lite-1.5.0-linux-aarch32/providers/Hi3516D)
link_directories(<HI3516D_SDK_PATH>)
target_link_libraries(benchmark net micro_nnie nnie mpi VoiceEngine upvqe securec -lm -pthread)
Finally, we build the benchmark:
cd nnie && mkdir buid && cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=<MS_SRC_PATH>/mindspore/lite/cmake/himix200.toolchain.cmake -DPLATFORM_ARM32=ON -DPKG_PATH=<RUNTIME_PKG_PATH> ..
make
