Dataset
MindSpore Transformers currently supports multiple types of dataset loading methods, covering common open-source and custom scenarios. Specifically, it includes:
Megatron Datasets: Supports loading datasets in the Megatron-LM format, suitable for large-scale language model pre-training tasks.
HuggingFace Datasets: Compatible with the HuggingFace datasets library, making it convenient to access a wide range of public data resources from the community.
MindRecord Datasets: MindRecord is an efficient data storage and reading module provided by MindSpore. This module offers various methods to help users convert different public datasets into the MindRecord format, as well as tools for reading, writing, and retrieving data from MindRecord files.
Megatron Dataset
Megatron dataset is an efficient data format designed for large-scale distributed language model pre-training scenarios, widely used within the Megatron-LM framework. These datasets are typically preprocessed and serialized into binary formats (such as .bin or .idx files), accompanied by specific indexing mechanisms to enable efficient parallel loading and data partitioning in distributed cluster environments.
The following sections will explain how to generate .bin and .idx files, as well as how to use Megatron datasets in training tasks.
Data Preprocessing
MindSpore Transformers provides a data preprocessing script, preprocess_indexed_dataset.py, which is used to convert raw text data in json format into .bin and .idx files.
If the raw text data is not in json format, users need to preprocess and convert it into the appropriate format themselves.
Below is an example of a json format file:
{"src": "www.nvidia.com", "text": "The quick brown fox", "type": "Eng", "id": "0", "title": "First Part"}
{"src": "The Internet", "text": "jumps over the lazy dog", "type": "Eng", "id": "42", "title": "Second Part"}
...
The descriptions for each data field are as follows:
Field Name |
Description |
Required |
|---|---|---|
text |
Raw text data |
Yes |
id |
Unique identifier (in order) |
No |
src |
Data source |
No |
type |
Language type |
No |
title |
Data title |
No |
The following example demonstrates how to convert the wikitext-103 dataset into a Megatron dataset format:
Download the
wikitext-103dataset: LinkGenerate a
jsonformat data fileThe original text of the
wikitext-103dataset looks like this:= Valkyria Chronicles III = Valkyria Chronicles III is a tactical role-playing game developed by Sega for the PlayStation Portable. The game was released in Japan on January 27, 2011. = Gameplay = The game is similar to its predecessors in terms of gameplay...
You need to preprocess the original text into the following format and save it as a
jsonfile:{"id": 0, "text": "Valkyria Chronicles III is a tactical role-playing game..."} {"id": 1, "text": "The game is similar to its predecessors in terms of gameplay..."} ...Download the model's vocabulary file
Since different models use different vocabulary files, you need to download the corresponding vocabulary file for the training model. Taking the
Llama3model as an example, download the tokenizer.model for data preprocessing.Generate
.binand.idxdata filesRun the data preprocessing script preprocess_indexed_dataset.py to convert the original text data into corresponding token IDs using the model's tokenizer.
The script accepts the following parameters:
Parameter Name
Description
input
Path to the
jsonformat fileoutput-prefix
Prefix for the
.binand.idxdata filestokenizer-type
Type of tokenizer used by the model
vocab-file
Path to the model’s tokenizer file (
tokenizer.model/vocab.json)merges-file
Path to the model’s tokenizer merges file (
merge.txt)add_bos_token
Whether to add a
bos_token(beginning of sequence token) to the vocabularyadd_eos_token
Whether to add an
eos_token(end of sequence token) to the vocabularyseq-length
Set the sequence length for dataset samples
pad_or_stitch
Choose to either
padorstitchsamplesregister_path
Set the code directory of outer tokenizer. Take effects only when
tokenizer-type='AutoRegister'auto_register
Set the import path of outer tokenizer. Take effects only when
tokenizer-type='AutoRegister'The optional value of
tokenizer-typeis 'LlamaTokenizer', 'LlamaTokenizerFast' and 'AutoRegister'. When it's set to 'LlamaTokenizer' or 'LlamaTokenizerFast', the corresponding public tokenizer class in MindSpore Transformers will be called. When it's set to 'AutoRegister', outer tokenizer class specified byregister_pathandauto_registerwill be applied.Take public tokenizer class
LlamaTokenizerFastfor example, execute the following command to preprocess the dataset:python mindformers/tools/dataset_preprocess/preprocess_indexed_dataset.py \ --input /path/data.json \ --output-prefix /path/megatron_data \ --tokenizer-type LlamaTokenizerFast \ --vocab-file /path/tokenizer.model \ --add_bos_token True \ --add_eos_token True \ --pad_or_stitch stitch \ --seq-length 8192
Take outer tokenizer class Llama3Tokenizer for example, make sure local MindSpore Transformers repository has 'research/llama3_1/llama3_1_tokenizer.py', and execute the following command to preprocess the dataset:
python mindformers/tools/dataset_preprocess/preprocess_indexed_dataset.py \ --input /path/data.json \ --output-prefix /path/megatron_data \ --tokenizer-type AutoRegister \ --vocab-file /path/tokenizer.model \ --add_bos_token True \ --add_eos_token True \ --pad_or_stitch stitch \ --seq-length 8192 \ --register_path research/llama3_1 \ --auto_register llama3_1_tokenizer.Llama3Tokenizer
Model Pre-training
MindSpore Transformers recommends using Megatron datasets for model pre-training. Based on the Data Preprocessing steps, you can generate the required pre-training dataset. The following explains how to configure and use Megatron datasets in the configuration file.
Prepare the
parallel_speed_up.jsonfileMegatron dataset relies on the
dataset_broadcast_opt_levelfeature for data broadcasting. For more details, refer to the documentation. Therefore, you need to create aparallel_speed_up.jsonfile with the following content:{ "dataset_broadcast_opt_level": 3 }
At the same time, add the following fields to the model configuration file:
context: ascend_config: parallel_speed_up_json_path: "/path/to/parallel_speed_up.json"
Modify the model configuration file
To use the Megatron dataset in model pre-training tasks, mainly modify the
train_datasetsection in the configuration file.train_dataset: &train_dataset data_loader: type: BlendedMegatronDatasetDataLoader datasets_type: "GPTDataset" sizes: - 1000 # Number of training dataset samples - 0 # Number of testing dataset samples (currently unsupported) - 0 # Number of evaluation dataset samples (currently unsupported) config: # GPTDataset configuration options seed: 1234 # Random seed for data sampling split: "1, 0, 0" # Ratio of training, testing, and evaluation datasets (currently unsupported) seq_length: 8192 # Sequence length of data returned by the dataset eod_mask_loss: True # Whether to compute loss at end-of-document (EOD) tokens reset_position_ids: True # Whether to reset position_ids at EOD tokens create_attention_mask: True # Whether to return attention_mask reset_attention_mask: True # Whether to reset attention_mask at EOD tokens, returning a staircase-shaped mask create_compressed_eod_mask: False # Whether to return a compressed attention_mask eod_pad_length: 128 # Length of the compressed attention_mask eod: 0 # Token ID of the EOD token in the dataset pad: 1 # Token ID of the pad token in the dataset data_path: # Sampling ratio and paths for Megatron datasets - '0.3' # Ratio of dataset1 - "/path/megatron_data1" # Path to bin file of dataset1 excluding the .bin suffix - '0.7' # Ratio of dataset2 - "/path/megatron_data2" # Path to bin file of dataset2 excluding the .bin suffix input_columns: ["input_ids", "labels", "loss_mask", "position_ids", "attention_mask"] construct_args_key: ["input_ids", "labels", "loss_mask", "position_ids", "attention_mask"] parallel: full_batch: False dataset_strategy: [[*dp, 1], [*dp, 1], [*dp, 1], [*dp, 1], [*dp, 1, 1, 1]] # *dp means same value as data_parallel model_config: input_sliced_sig: True
Below are the descriptions for each configuration option of the
GPTDatasetin the dataset:Parameter Name
Description
seed
Random seed for dataset sampling. Megatron datasets use this value to randomly sample and concatenate samples. Default:
1234seq_length
Sequence length of data returned by the dataset. Should be consistent with the sequence length of the training model.
eod_mask_loss
Whether to compute loss at the end-of-document (EOD) token. Default:
Falsecreate_attention_mask
Whether to return an attention_mask. Default:
Truereset_attention_mask
Whether to reset the attention_mask at EOD tokens, returning a staircase-shaped attention_mask. Effective only if
create_attention_mask=True. Default:Falsecreate_compressed_eod_mask
Whether to return a compressed attention_mask. Has higher priority than
create_attention_mask. Default:Falseeod_pad_length
Length of the compressed attention_mask. Effective only if
create_compressed_eod_mask=True. Default:128eod
Token ID of the EOD token in the dataset
pad
Token ID of the pad token in the dataset
data_path
List, every two consecutive elements (number, string) are considered as a dataset, represent ratio of the dataset and the path to its bin file excluding
.binsuffix respectively. The sum of datasets' ratios should be equal to 1.In addition, the Megatron dataset also depends on configurations such as
input_columns,construct_args_key, andfull_batch. For more details, refer to the configuration file documentation.Here, we only explain how to configure them in different scenarios:
When
create_compressed_eod_mask=True:
train_dataset: &train_dataset input_columns: ["input_ids", "labels", "loss_mask", "position_ids", "actual_seq_len"] construct_args_key: ["input_ids", "labels", "loss_mask", "position_ids", "actual_seq_len"] parallel: full_batch: False dataset_strategy: [[*dp, 1], [*dp, 1], [*dp, 1], [*dp, 1], [*dp, 1]] # *dp means same value as data_parallel
When
create_compressed_eod_mask=Falseandcreate_attention_mask=True:
train_dataset: &train_dataset input_columns: ["input_ids", "labels", "loss_mask", "position_ids", "attention_mask"] construct_args_key: ["input_ids", "labels", "loss_mask", "position_ids", "attention_mask"] parallel: full_batch: False dataset_strategy: [[*dp, 1], [*dp, 1], [*dp, 1], [*dp, 1], [*dp, 1, 1, 1]] # *dp means same value as data_parallel
When
create_compressed_eod_mask=Falseandcreate_attention_mask=False:
train_dataset: &train_dataset input_columns: ["input_ids", "labels", "loss_mask", "position_ids"] construct_args_key: ["input_ids", "labels", "loss_mask", "position_ids"] parallel: full_batch: False dataset_strategy: [[*dp, 1], [*dp, 1], [*dp, 1], [*dp, 1]] # *dp means same value as data_parallel
Start Model Pre-training
After modifying the dataset and parallel-related configurations in the model configuration file, you can refer to the model documentation to launch the model pre-training task. Here, we take the Llama3_1 model documentation as an example.
HuggingFace Datasets
Currently, the dataset loading functionality has been integrated with the ModelScope Open-Source Community and the HuggingFace Community, supporting online dataset loading and preprocessing. Additionally, datasets can be packed to enhance model training efficiency.
Usage Instructions
HuggingFace datasets support online and offline loading of datasets from both the HuggingFace community and the MoLo open-source community. Below is an introduction to environment preparation, the dataset loading process, and how to configure the use of HuggingFace datasets in configuration files.
Integrating with Open-Source Communities
Integrating with HuggingFace Community
To use datasets from the HuggingFace community, follow these steps:
Environment Setup
The environment variable
HF_ENDPOINTcontrols the remote repository used by HuggingFace. By default, it is set tohttps://huggingFace.co. For users in China, it is recommended to configure it to the mirror addressexport HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com.Install Dependencies
pip install datasets
Integrating with ModelScope Open-Source Community
To use datasets from the ModelScope Open-Source Community, follow these steps:
Environment Setup
The environment variable
OPENMIND_HUB_ENDPOINTcontrols the remote repository used by the ModelScope Open-Source Community. Defaults toexport OPENMIND_HUB_ENDPOINT=https://telecom.openmind.cnwhen not configured.Install Dependencies
git clone https://gitee.com/openmind-ai/openmind-hub.git cd openmind-hub pip install -e . cd .. git clone https://gitee.com/foundation-models/openmind-datasets.git cd openmind-datasets pip install -e . cd ..
When the openmind-datasets component is installed in the environment, the default interface is the Modelers open source community, if you want to interface with HuggingFace, the environment variable
USE_OMcan control which community to interface with, the default value isONfor the Modelers community, change it toOFFto interface with the HuggingFace community.
Dataset Loading Process
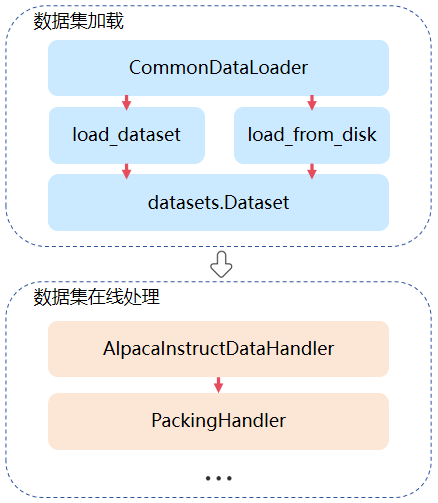
The online dataset loading and processing functionality is primarily implemented through CommonDataLoader. The data loading part can be customized via configuration files, with detailed configuration instructions available in the dataloader parameter description. The online loading module requires users to implement customizations for different datasets. For example, the AlpacaInstructDataHandler class can be used to preprocess the alpaca dataset. For more information, please refer to Custom Data Handler.
The parameters such as seq_length and tokenizer used in the examples below are all from the qwen2.5 model.
Since the qwen2.5 model is located in the research directory, the --register_path parameter needs to be used when launching the task.
Users can adjust these parameters according to their actual situation.
dataloader Parameter Description
The online dataset loading feature is enabled by configuring the data_loader in the configuration file. Below is an example configuration for online dataset loading:
train_dataset: &train_dataset
input_columns: &input_columns ["input_ids", "labels", "loss_mask", "position_ids", "attention_mask"]
construct_args_key: *input_columns
data_loader:
type: CommonDataLoader
load_func: 'load_dataset'
shuffle: False
split: "train"
path: "llm-wizard/alpaca-gpt4-data"
packing: pack
handler:
- type: AlpacaInstructDataHandler
tokenizer:
model_max_length: 131072
bos_token: null
eos_token: "<|im_end|>"
unk_token: null
pad_token: "<|endoftext|>"
vocab_file: "/path/vocab.json" # qwen2.5
merges_file: "/path/merges.txt" # qwen2.5
auto_register: qwen2_5_tokenizer.Qwen2Tokenizer
type: Qwen2Tokenizer
seq_length: 8192
prompt_key: "conversations"
output_columns: ["input_ids", "labels"]
is_dynamic: False
- type: PackingHandler
seq_length: 8192
output_columns: ["input_ids", "labels", "actual_seq_len"]
adaptor_config:
compress_mask: False
column_names: *input_columns
Parameter descriptions for data_loader are as follows:
Parameter Name |
Description |
Type |
|---|---|---|
type |
Fixed as |
str |
packing |
Packing configuration when processing datasets with |
str |
load_func |
The function used to load datasets. Options are |
str |
path |
When |
str |
data_files |
When |
str |
handler |
Multiple |
list |
adaptor_config |
Dataset-related configuration during model training. Currently supports |
dict |
shuffle |
Indicates whether random sampling is enabled when loading the dataset. |
bool |
column_names |
Specifies the column names returned by the dataset. If not set, all columns are returned. |
list |
is_dynamic |
Indicates whether the dataset returns dynamic-length data. Default is |
bool |
In addition to the above configurations, all parameters from the datasets.load_dataset interface are supported with the same meanings and functions.
When packing is configured, the dataset returns an actual_seq_len column. For more information, refer to the actual_seq_qlen and actual_seq_kvlen parameter descriptions in the documentation.
Feature Introduction
Dynamic Sequence Length Fine-Tuning
CommonDataLoader supports dynamic shape fine-tuning using HuggingFace datasets, which can be loaded online or offline. Below, we use the alpaca dataset as an example to demonstrate the configuration for dynamic shape fine-tuning.
Online Loading
The online dataset name is
llm-wizard/alpaca-gpt4-data. You can search and download it from the HuggingFace official website or load it directly using the online name.Example configuration for online loading:
train_dataset: &train_dataset input_columns: &input_columns ["input_ids", "labels"] dynamic_batch: True # Enable dynamic shape divisor: 32 # With divisor and remainder configured, seq_length in dynamic shape will become a multiple of divisor and the sum of remainder remainder: 1 data_loader: type: CommonDataLoader shuffle: True split: "train" # Subset name of the online dataset path: "llm-wizard/alpaca-gpt4-data" # Online dataset name handler: - type: AlpacaInstructDataHandler tokenizer: model_max_length: 131072 bos_token: null eos_token: "<|im_end|>" unk_token: null pad_token: "<|endoftext|>" vocab_file: "/path/vocab.json" # qwen2.5 merges_file: "/path/merges.txt" # qwen2.5 auto_register: qwen2_5_tokenizer.Qwen2Tokenizer type: Qwen2Tokenizer seq_length: 8192 prompt_key: "conversations" output_columns: *input_columns is_dynamic: True seed: 0 num_parallel_workers: 8 python_multiprocessing: False drop_remainder: True repeat: 1 numa_enable: False prefetch_size: 1
For parameter descriptions in
train_dataset, please refer to the documentation.AlpacaInstructDataHandleris an online processing script developed for thealpacadataset. If using a different dataset, you need to implement a custom data handler by referring to the Custom Data Handler guide.
Offline Loading
For offline loading, you need to prepare the JSON files of the
alpacadataset. The offline configuration differs from the online configuration only in the following parameters:train_dataset: data_loader: path: "json" # loading datasets using the load_dataset interface data_files: '/path/alpaca_gpt4_data.json' # the file path of the alpaca dataset
After configuring the dataset loading method, you also need to set is_dynamic=True in the model configuration to enable dynamic shape training for the model.
model_config:
is_dynamic: True
Since dynamic shapes may lead to operator compilation caching, it is recommended to set the following environment variables to limit the number of cached compilations when running in a memory-constrained environment. This helps prevent out-of-memory issues:
export ACLNN_CACHE_LIMIT=10
export MS_DEV_RUNTIME_CONF="aclnn_cache_queue_length:64"
The
ACLNN_CACHE_LIMITparameter description can be found in the documentation.MS_DEV_RUNTIME_CONFis a parameter in MindSpore for setting the operator cache queue length. The value64represents the length of the sequence, which defaults to1024. This can be adjusted based on the actual environment. Setting the value too small may affect model training performance.
After completing all the configurations above, you can proceed with dynamic shape fine-tuning by referring to the documentation for the specific model you are using.
Custom Data Handler
Users can define custom data handlers to apply various preprocessing logic to the loaded dataset.
Handler Parameter Description
Parameter Name
Description
Type
type
Custom data handler name. A custom handler must inherit from
BaseInstructDataHandler.str
tokenizer_name
Name of the tokenizer used.
str
tokenizer
Tokenizer configuration parameters. Can be a dictionary, string, or a
tokenizerobject. Takes lower priority thantokenizer_name.dict/str
seq_length
Maximum sequence length, usually the same as the model's sequence length.
int
output_columns
Column names of the processed data returned after preprocessing.
list
prompt_key
Column name for data after applying prompt processing.
str
Development Sample 1
The custom data handler is usually placed in the
mindformers/dataset/handlerdirectory, and the customized one needs to inherit the abstract base classBaseInstructDataHandler. You need to implementformat_funcandtokenize_funcmethods, which preprocess each data loaded. Refer toalpaca_handler.py.@MindFormerRegister.register(MindFormerModuleType.DATA_HANDLER) class XXXInstructDataHandler(BaseInstructDataHandler): def format_func(self, example): # Custom data format conversion def tokenize_func(self, example): # Custom tokenizer split word processing
The
BaseInstructDataHandlerprovides an implementation of the entryhandlermethod by default, which is used to iterate over each piece of data for data preprocessing. Theformat_funcis used to implement how to convert the raw data into the desired data format, and thetokenize_funcmethod is used to take the processed data and perform a customized tokenization. The input parameterexamplein the example is each of the samples obtained.Development Sample 2
If you want to process the data directly for the whole dataset instead of processing each piece of data in batches, you can implement the entry
handlemethod in custom handler, and you will get the complete dataset, as shown below:def handle(self, dataset): """data handler""" return dataset.rename_columns({"content":"prompt","summary":"answer"})
alpaca Dataset Sample
Modify the task configuration file finetune_qwen2_5_0_5b_8k.yaml.
Modify the following parameters:
train_dataset: &train_dataset input_columns: &input_columns ["input_ids", "labels"] data_loader: type: CommonDataLoader shuffle: True split: "train" path: "llm-wizard/alpaca-gpt4-data" handler: - type: AlpacaInstructDataHandler tokenizer: model_max_length: 131072 bos_token: null eos_token: "<|im_end|>" unk_token: null pad_token: "<|endoftext|>" vocab_file: "/path/vocab.json" # qwen2.5 merges_file: "/path/merges.txt" # qwen2.5 auto_register: qwen2_5_tokenizer.Qwen2Tokenizer type: Qwen2Tokenizer seq_length: 8192 prompt_key: "conversations" output_columns: *input_columns seed: 0 num_parallel_workers: 8 python_multiprocessing: False drop_remainder: True repeat: 1 numa_enable: False prefetch_size: 1
The rest of the parameters can be described in "model training configuration" and "model evaluation configuration" in Configuration File Description.
Custom data handler:
@MindFormerRegister.register(MindFormerModuleType.DATA_HANDLER) class AlpacaInstructDataHandler(BaseInstructDataHandler): def format_func(self, example): """format func""" source = PROMPT_INPUT.format_map(example) \ if example.get(self.input_key, "") != "" \ else PROMPT_NO_INPUT.format_map(example) target = example.get(self.output_key) formatted_example = [ { "from": self.user_role, "value": source, }, { "from": self.assistant_role, "value": target, }, ] return formatted_example def tokenize_func(self, messages): """tokenize func""" conversation = self.gen_prompt(messages) sep = self.template.sep + self.assistant_role + ": " # Tokenize conversations rounds = conversation.split(self.template.sep2) ids = [self.tokenizer.bos_token_id] mask = [1] for _, rou in enumerate(rounds): if rou == "": break conv_out = self.tokenizer(rou) ids.extend(conv_out['input_ids'][1:]) mask.extend(conv_out['attention_mask'][1:]) d = {'input_ids': ids, 'attention_mask': mask} # pylint: disable=W0212 if not self.dynamic: d = self.tokenizer._pad(d, max_length=self.seq_length + 1, padding_strategy='max_length') input_id = d['input_ids'][:self.seq_length + 1] target = np.array(d['input_ids']) total_len = int(np.not_equal(target, self.tokenizer.pad_token_id).sum()) cur_len = 1 target[:cur_len] = self.ignore_token_id for _, rou in enumerate(rounds): if rou == "": break parts = rou.split(sep) if len(parts) != 2: break parts[0] += sep round_len = len(self.tokenizer(rou)['input_ids']) - 1 instruction_len = len(self.tokenizer(parts[0])['input_ids']) - 3 target[cur_len: cur_len + instruction_len] = self.ignore_token_id cur_len += round_len if self.dynamic: return { "input_ids": input_id, "labels": target[:len(input_id)].tolist() } target[cur_len:] = self.ignore_token_id if cur_len < self.seq_length + 1: if cur_len != total_len: target[:] = self.ignore_token_id else: target = target[:self.seq_length + 1] label = target.tolist() return { "input_ids": input_id, "labels": label, }
ADGEN Dataset Sample
Modify the following parameters:
train_dataset: &train_dataset data_loader: type: CommonDataLoader path: "HasturOfficial/adgen" split: "train" shuffle: True handler: - type: AdgenInstructDataHandler phase: "train" version: 3 column_names: ["prompt", "answer"] tokenizer: type: ChatGLM3Tokenizer vocab_file: "/path/to/tokenizer.model" input_columns: ["input_ids", "labels"] max_source_length: 1024 max_target_length: 1023 ignore_pad_token_for_loss: True num_parallel_workers: 8 python_multiprocessing: False drop_remainder: True batch_size: 8 repeat: 1 numa_enable: False prefetch_size: 1 seed: 0
The rest of the parameters can be described in "model training configuration" and "model evaluation configuration" in Configuration File Description.
Custom adgen_handler:
@MindFormerRegister.register(MindFormerModuleType.DATA_HANDLER) class AdgenInstructDataHandler(BaseInstructDataHandler): """agden data handler""" def handle(self, dataset): """data handler""" return dataset.rename_columns({"content": "prompt", "summary": "answer"})
Dataset Packing
Configuring PackingHandler in CommonDataLoader allows for packing processing of the data. Currently, the original data needs to be processed into input_ids and labels that can be fed into the model during the preprocessing step.
Parameter Description
Parameter Name
Description
Type
type
Fixed as
PackingHandler. This module supports packing data. Whenpacking=packorpacking=truncateis configured in dataloader, it performs non-truncating and truncating concatenation of the data, respectively.str
seq_length
Maximum sequence length of the data after packing.
int
pad_token
Token ID used for padding
input_idswhen the packed sample does not reach the maximum length. Default value is 0.int
ignore_token
Token ID used for padding
labelswhen the packed sample does not reach the maximum length. Default value is -100.int
Packing Example
By following the configuration below, the
alpacadataset can be preprocessed to achieve online packing.train_dataset: &train_dataset input_columns: &input_columns ["input_ids", "labels", "loss_mask", "position_ids", "attention_mask"] construct_args_key: *input_columns data_loader: type: CommonDataLoader shuffle: False split: "train" path: "llm-wizard/alpaca-gpt4-data" packing: pack handler: - type: AlpacaInstructDataHandler tokenizer: model_max_length: 131072 bos_token: null eos_token: "<|im_end|>" unk_token: null pad_token: "<|endoftext|>" vocab_file: "/path/vocab.json" # qwen2.5 merges_file: "/path/merges.txt" # qwen2.5 auto_register: qwen2_5_tokenizer.Qwen2Tokenizer type: Qwen2Tokenizer seq_length: 8192 prompt_key: "conversations" output_columns: ["input_ids", "labels"] - type: PackingHandler seq_length: 8192 output_columns: ["input_ids", "labels", "actual_seq_len"] adaptor_config: compress_mask: False seed: 0 num_parallel_workers: 8 python_multiprocessing: False drop_remainder: True repeat: 1 numa_enable: False prefetch_size: 1
Using the above configuration file to process the alpaca dataset will execute the following steps:
The raw text data will be processed into
input_idsandlabelsusingAlpacaInstructDataHandlerand thetokenizerofqwen2.5.PackingHandlerwill be used to perform packing on the processedinput_idsandlabels, resulting in concatenatedinput_idsandlabelsup to theseq_length. Theactual_seq_lenrefers to the sequence length of each sub-sample in the concatenated sample. During training, this parameter will be used to generate the corresponding data mask.If
compress_mask=Falseis set inadaptor_config, a complete data mask will be returned during training. Otherwise,actual_seq_lenwill be returned.
Offline Dataset Processing
In addition to supporting online dataset loading and processing, CommonDataLoader also supports offline dataset processing and saving.
The datasets_preprocess.py script can be used to process Huggingface datasets offline and save them.
Parameter Description
Parameter Name
Description
Type
config
Configuration file for offline data processing, which is used in the same way as online processing. Refer to dataloader for details.
str
save_path
Path where the preprocessed dataset will be saved.
str
register_path
Registration path for the model API, which includes the Python files related to the model, typically the model folder under the
researchdirectory.int
Usage Example
You can use the configuration file provided in the dataset packing example and execute the following command.
python toolkit/data_preprocess/huggingface/datasets_preprocess.py \ --config data_process.yaml \ --save_path /path/processed_data \ --register_path research/qwen2_5
If you need to load the saved dataset, you should modify the YAML configuration as follows:
train_dataset: &train_dataset input_columns: &input_columns ["input_ids", "labels", "loss_mask", "position_ids", "attention_mask"] construct_args_key: *input_columns data_loader: type: CommonDataLoader shuffle: False load_func: "load_from_disk" path: "/path/processed_data" adaptor_config: compress_mask: False
MindRecord Dataset
MindRecord is an efficient data storage and reading module provided by MindSpore. It reduces disk IO and network IO overhead, resulting in a better data loading experience. For more detailed feature introductions, refer to the documentation. Here, we only cover how to use MindRecord in MindSpore Transformers model training tasks.
The following example uses qwen2_5-0.5b fine-tuning to explain related functionalities.
Data Preprocessing
Download the
alpacadataset: LinkExecute the data processing script to convert the
alpacadataset into a dialogue format:python research/qwen2/alpaca_converter.py \ --data_path /path/alpaca_data.json \ --output_path /path/alpaca-data-messages.json
Here,
data_pathrefers to the path where the downloadedalpacadataset is stored, andoutput_pathrefers to the save path for the generated dialogue format data file.Execute the script to convert the dialogue format data file into MindRecord format:
python research/qwen2/qwen2_preprocess.py \ --dataset_type 'qa' \ --input_glob /path/alpaca-data-messages.json \ --vocab_file /path/vocab.json \ --merges_file /path/merges.txt \ --seq_length 32768 \ --output_file /path/alpaca-messages.mindrecord
The script parameters are explained as follows:
dataset_type: Type of data preprocessing. For the alpaca dataset, set this toqa.input_glob: Path to the dialogue format data file.vocab_file: Path to thevocab.jsonfile of the qwen2 model.merges_file: Path to themerges.txtfile of the qwen2 model.seq_length: Sequence length for generating MindRecord data.output_file: Save path for the generated MindRecord data.
The
vocab_fileandmerges_filecan be obtained from the qwen2 model repository on the HuggingFace community.
Model Fine-tuning
Following the above data preprocessing steps, you can generate a MindRecord dataset for fine-tuning the qwen2_5-0.5b model. Below is an introduction on how to use the generated data file to start the model fine-tuning task.
Modify the model configuration file
The
qwen2_5-0.5bmodel fine-tuning uses the finetune_qwen2_5_0.5b_8k.yaml configuration file. Modify the dataset section as follows:train_dataset: &train_dataset data_loader: type: MindDataset dataset_dir: "/path/alpaca-messages.mindrecord" shuffle: True
When using the MindRecord dataset in a model training task, the following configurations in
data_loaderneed to be modified:type: Type of data_loader. Set toMindDatasetwhen using MindRecord datasets.dataset_dir: Path to the MindRecord data files.shuffle: Whether to randomly sample data samples during training.
Start Model Fine-tuning
After modifying the dataset and parallel-related configurations in the model configuration file, you can refer to the model documentation to launch the fine-tuning task. Here, we take the Qwen2_5 model documentation as an example.
Multi-source Datasets
The native MindSpore dataset loading module MindDataset has performance bottlenecks when loading and sampling multiple MindRecord datasets.
Therefore, MindSpore Transformers implements the MultiSourceDataLoader to achieve efficient loading and sampling across multiple datasets.
The multi-source dataset functionality is mainly enabled by modifying the data_loader configuration in the config file. Below is an example:
train_dataset: &train_dataset
data_loader:
type: MultiSourceDataLoader
data_source_type: random_access
shuffle: True
dataset_ratios: [0.2, 0.8]
samples_count: 1000
nums_per_dataset: [2000]
sub_data_loader_args:
stage: 'train'
column_names: ["input_ids", "target_ids", "attention_mask"]
sub_data_loader:
- type: MindDataset
dataset_files: "/path/alpaca-messages.mindrecord"
- type: MindDataset
dataset_files: "/path/alpaca-messages.mindrecord"
load_indices_npz_path: '/path/index.npz'
save_indices_npz_path: '/path/index.npz'
The shuffle setting affects two parameters: shuffle_dataset and shuffle_file:
shuffle_datasetindicates random sampling at the sub-dataset level.shuffle_fileindicates random sampling at the sample level.
The effects of different shuffle values are as follows:
shuffle |
shuffle_dataset |
shuffle_file |
|---|---|---|
True |
True |
True |
False |
False |
False |
infile |
False |
True |
files |
True |
False |
global |
True |
True |
Other configuration parameters are explained below:
Parameter |
Description |
Type |
|---|---|---|
dataset_ratios |
Sampling ratios for each sub-dataset; sum of all equals 1 |
list |
samples_count |
Number of samples from each sub-dataset, effective only when |
int |
nums_per_dataset |
Number of samples per sub-dataset, effective when |
list |
sub_data_loader_args |
Common configurations for each sub-dataset, effective during sub-dataset construction |
dict |
sub_data_loader |
Configuration for each sub-dataset, same as |
list |
load_indices_npz_path |
Path to load data index file |
str |
save_indices_npz_path |
Path to save data index file |
str |