Introduction to MindSpore Elec
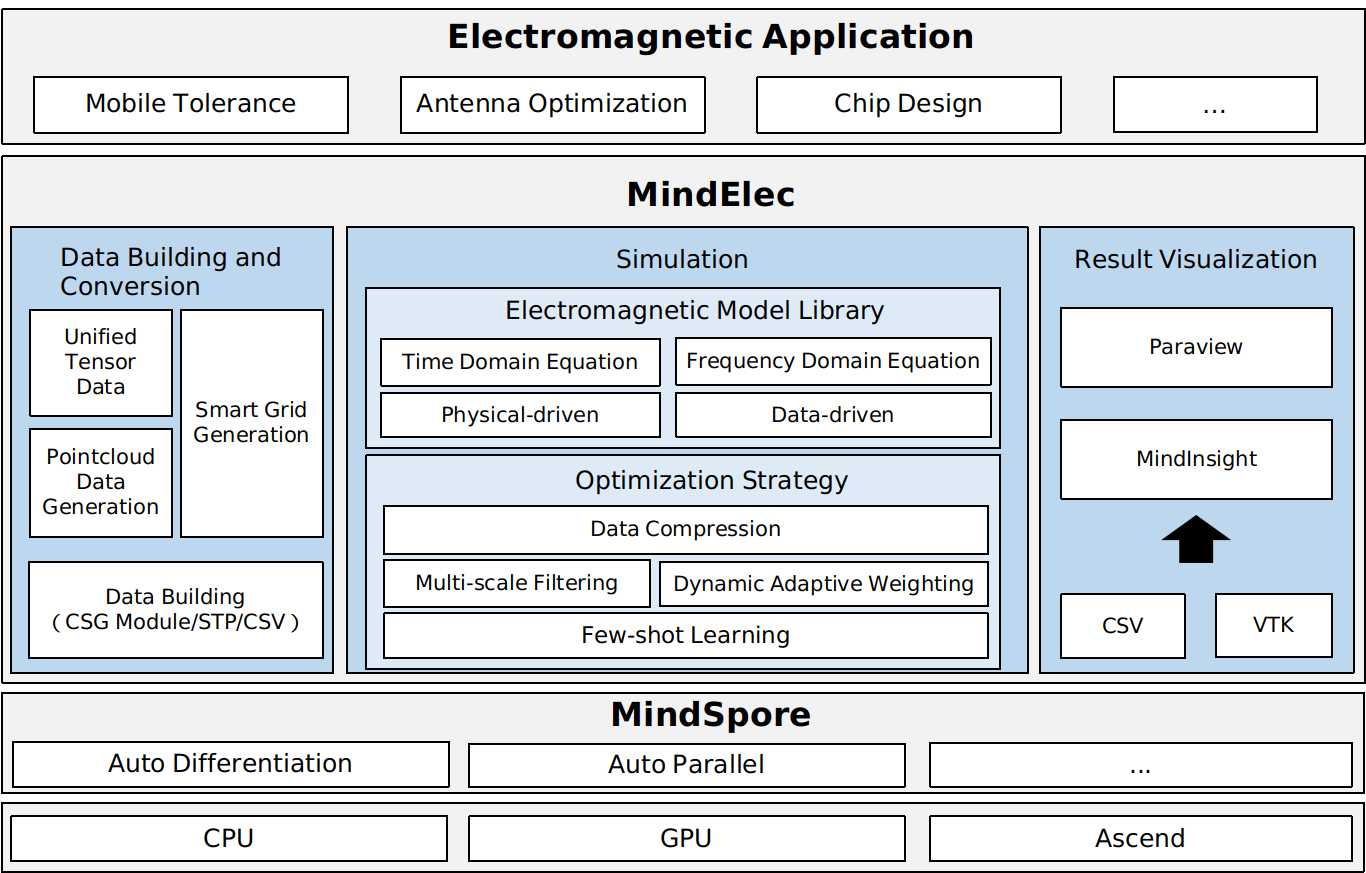
MindSpore Elec is an end-to-end supported AI electromagnetic simulation suite, consisting of data construction and conversion, simulation calculation, and result visualization.
Electromagnetic simulation refers to simulating the propagation characteristics of electromagnetic waves in objects or space through computation. It is widely used in scenarios such as mobile phone tolerance simulation, antenna optimization, and chip design. Conventional numerical methods, such as finite difference and finite element, require mesh segmentation and iterative computation. The simulation process is complex and the computation time is long, which cannot meet the product design requirements. With the universal approximation theorem and efficient inference capability, the AI method can improve the simulation efficiency.
Currently, Huawei has achieved phase achievements in the tolerance scenario of Huawei mobile phones. Compared with the commercial simulation software, the S parameter error of AI electromagnetic simulation is about 2%, and the end-to-end simulation speed is improved by more than 10 times.
Code repository address: <https://gitee.com/mindspore/mindscience/tree/r0.2.0/MindElec>
Data Building and Conversion
Supports geometric construction in constructive solid geometry (CSG) mode, such as the intersection set, union set, and difference set of rectangles and circles, and also supports efficient tensor conversion of CST and STP data (data formats supported by commercial software such as CST). In the future, we will support smart grid division for traditional scientific computing.
Simulation
Electromagnetic Model Library
Provides the physical-driven and data-driven AI electromagnetic models. Physical-driven model refers to network training that does not require additional label data. Only equations and initial boundary conditions are required. Data-driven model refers to training that requires data generated through simulation or experiments. Compared with the data-driven model, the physical-driven model has the advantage of avoiding problems such as cost and mesh independence caused by data generation. The disadvantage of the physical-driven model is that the expression form of the equation needs to be specified and technical challenges such as point source singularity, multi-task loss function, and generalization need to be overcome.
Optimization strategy
Provides a series of optimization strategies to improve physical-driven and data-driven model accuracy and reduce training costs. Data compression can effectively reduce the storage and computation workload of the neural network. Multi-scale filtering and dynamic adaptive weighting can improve the model accuracy and overcome the problems such as point source singularity. Few-shot learning will be completed subsequently to reduce the training data volume and training cost.
Result Visualization
The simulation results, such as the S parameters or electromagnetic fields, can be saved in the CSV or VTK files. MindSpore Insight can display the loss function changes during the training process and display the results on the web page in the form of images. ParaView is the third-party open-source software and can dynamically display advanced functions such as slicing and flipping.
Installation
Application
API References
RELEASE NOTES