MindSpore Lite Cloud-side Documentation
MindSpore Lite inference comprises two components: cloud-side inference and device-side inference. This document primarily introduces MindSpore Lite cloud-side inference. For device-side inference, please refer to the Device-side Inference Documentation .
Usage Scenarios
MindSpore Lite cloud-side inference is primarily designed for server-side devices. It offers compatibility with model structures exported from the MindSpore training framework and various open-source formats including ONNX, TFLite, and Pb. This version is applicable to Ascend cards (such as Atlas 300I Duo, Atlas 800I A2, Atlas 800I A3 series) and CPU hardware based on X86/Arm architectures. MindSpore Lite has also implemented targeted optimizations and adaptations for various algorithmic scenarios. Its current features and optimizations primarily focus on multi-modal generation, speech recognition, speech synthesis, autonomous driving, vector models, and traditional computer vision domains.
Advantages
MindSpore Lite effectively reduces operator dispatch latency through whole-graph sinking during model inference, thereby enhancing model inference performance;
For multi-modal generative algorithm models, MindSpore Lite supports key capabilities including multiple cache mechanisms, quantization, shared memory, and multi-dimensional hybrid parallelism. For Ascend hardware, MindSpore Lite enables user-defined operator integration;
For speech-related algorithm models, MindSpore Lite supports key capabilities such as zero-copy I/O data processing;
For autonomous driving models, MindSpore Lite supports hybrid scheduling of single operators and subgraphs during inference on Ascend hardware. This ensures subgraph-sinking inference performance while enabling rapid integration of custom operators for autonomous driving applications through hybrid scheduling.
Development Process
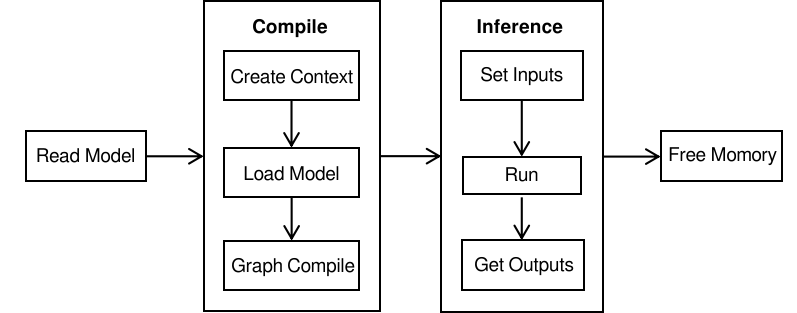
Using the MindSpore Lite inference framework primarily involves the following steps:
Model loading: You can directly load MindIR models exported from MindSpore training, or convert models exported from third-party frameworks into MindIR format using the MindSpore Lite conversion tool. These converted models can then be loaded via MindSpore Lite's interfaces.
Model compilation:
Create a configuration context: By creating a
Context, save some essential configuration parameters to guide graph compilation and model execution.Model loading: Before performing inference, the
Buildinterface of theModelmust be invoked to load the model. This process parses the cached file into a runtime model.Graph compilation: After model loading completes, the MindSpore Lite runtime compiles the graph. The model compilation phase consumes significant time, so it is recommended to create the model once, compile it once, and perform multiple inferences.
Model inference:
Input data must be padded before model execution.
Execute inference: Use the
Predictfunction of theModelfor model inference.Obtain the output: The
outputsparameter in thePredictinterface returns the inference results. By parsing theMSTensorobject, you can obtain the model's inference results along with the output data type and size.
Memory release: During the model compilation phase, resources such as resident memory, video memory, and thread pools are allocated. These resources must be released after model inference concludes to prevent resource leaks.