ms_function动静结合
Ascend GPU CPU 模型运行
概述
ms_function的作用是在PyNative模式下提升执行性能。在MindSpore框架中,PyNative模式(即动态图模式)下,用户可以使用完整的Python语法,更加简单方便地使用MindSpore进行网络调优。与此同时,PyNative模式也会导致一部分性能的损失。
ms_function支持在PyNative模式下,让被ms_function修饰的程序以静态图的方式来运行。ms_function会将修饰的程序通过静态编译的方式来生成可执行图,整体下发执行,从而提升该修饰部分的执行性能。
本文档主要介绍ms_function的使用方法和工作原理,以便您可以更有效地使用ms_function功能。
修饰独立函数
使用ms_function装饰器时,可以对独立定义的函数进行修饰。
[1]:
# pylint: disable=W0235,W0612
import numpy as np
import mindspore.ops as ops
from mindspore import context, Tensor, ms_function
@ms_function
def add_func(x, y):
return ops.add(x, y)
context.set_context(mode=context.PYNATIVE_MODE)
x = Tensor(np.ones([3, 3], dtype=np.float32))
y = Tensor(np.ones([3, 3], dtype=np.float32))
out = add_func(x, y)
print(out)
[[2. 2. 2.]
[2. 2. 2.]
[2. 2. 2.]]
修饰Cell的成员函数
使用ms_function装饰器时,可以对Cell的成员函数进行修饰。
[2]:
import numpy as np
import mindspore.nn as nn
import mindspore.ops as ops
from mindspore import context, Tensor, ms_function
class Add(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self):
super(Add, self).__init__()
@ms_function
def construct(self, x, y):
out = x * y
return out
context.set_context(mode=context.PYNATIVE_MODE)
x = Tensor(np.ones([3, 3], dtype=np.float32))
y = Tensor(np.ones([3, 3], dtype=np.float32))
grad_ops = ops.GradOperation(get_all=True)
net = Add()
grad_out = grad_ops(net)(x, y)
print(grad_out)
(Tensor(shape=[3, 3], dtype=Float32, value=
[[1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000],
[1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000],
[1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000]]), Tensor(shape=[3, 3], dtype=Float32, value=
[[1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000],
[1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000],
[1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000, 1.00000000e+000]]))
实现原理
本小节将介绍ms_function的实现原理,当你深入了解了ms_function的工作原理时,你将会更高效地使用ms_function。
以一个简单的动静结合的用例来说明,如下:
[3]:
import numpy as np
import mindspore.nn as nn
from mindspore import context, Tensor, ms_function
class Add(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self):
super(Add, self).__init__()
def construct(self, x):
x = x + x
x = x + x
return x
class Mul(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self):
super(Mul, self).__init__()
@ms_function
def construct(self, x):
x = x * x
x = x * x
return x
class Test(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self):
super(Test, self).__init__()
self.add = Add()
self.mul = Mul()
def construct(self, x):
x = self.add(x)
x = self.mul(x)
x = self.add(x)
return x
context.set_context(mode=context.PYNATIVE_MODE)
x = Tensor(np.ones([3, 3], dtype=np.float32))
net = Test()
out = net(x)
print(out)
[[1024. 1024. 1024.]
[1024. 1024. 1024.]
[1024. 1024. 1024.]]
该用例按照执行序,编译的方式如下图所示:
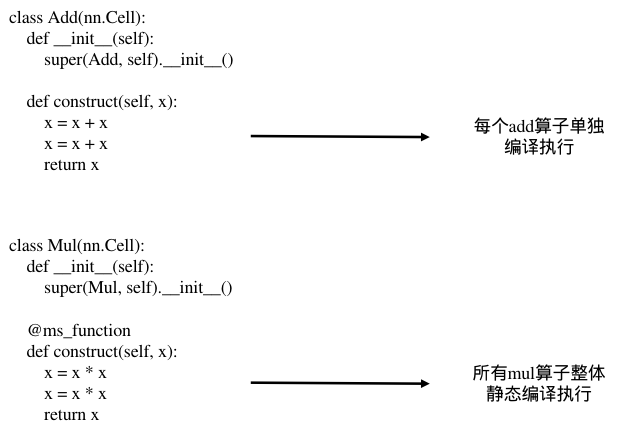
被ms_function修饰的函数将会按照静态图的方式进行编译和执行。如果网络涉及到反向求导,被ms_function修饰的部分也将以整图的形式来生成反向图,并与前后单个算子的反向图连成整体的反向图,下发执行。 其中,缓存的策略与静态图的缓存策略一致,相同的函数对象在输入Shape和Type信息一致时,编译的图结构将会被缓存。
使用须知
在使用ms_function来修饰函数,加速执行效率时,请注意以下几点:
ms_function修饰的函数须在静态图编译支持的语法范围内,包括但不限于数据类型等。
ms_function修饰的函数所支持的控制流语法,与静态图保持一致。其中,仅对固定循环次数或者分支条件的控制流结构具有加速效果。
在PyNative模式下使用ms_function功能时,非ms_function修饰的部分支持断点调试;被ms_function修饰的部分由于是以静态图的方式编译,不支持断点调试。
由于ms_function修饰的函数将按照静态图的方式编译执行,因此ms_function不支持修饰的函数中含有Hook算子,以及不支持修饰自定义Bprop函数等。
ms_function修饰的函数会受到静态图函数副作用的影响。
函数副作用指:当调用函数时,除了函数返回值之外,还对主调用函数产生的附加影响。例如修改全局变量(函数外的变量),修改函数的参数等。
场景1:
[4]:
import numpy as np
from mindspore import context, Tensor, ms_function
value = 5
@ms_function
def func(x, y):
out = x + y
value = 1
return out
context.set_context(mode=context.PYNATIVE_MODE)
x = Tensor(np.ones([3, 3], dtype=np.float32))
y = Tensor(np.ones([3, 3], dtype=np.float32))
func(x, y)
print(value)
5
该场景下,value是全局变量且在func函数中被修改。此时,如果用ms_function修饰func函数,全局变量value的值将不会被修改。原因是静态图编译时,会优化掉与返回值无关的语句。
场景2:
[5]:
import numpy as np
import mindspore.nn as nn
from mindspore import context, Tensor, ms_function
class Func(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self):
super(Func, self).__init__()
self.value = 5
@ms_function
def construct(self, x):
out = self.value + x
return out
context.set_context(mode=context.PYNATIVE_MODE)
x = Tensor(np.ones([3, 3], dtype=np.float32))
func = Func()
out = func(x)
func.value = 1
out = func(x)
print(out)
[[6. 6. 6.]
[6. 6. 6.]
[6. 6. 6.]]
该场景下,value是Func对象的参数,此时如果用ms_function修饰Func对象的construct成员函数。执行Func时将会以静态图的方式编译执行。由于静态图会缓存编译结果,第二次调用Func时,对value的修改将不会生效。



