Memory Management
Overview
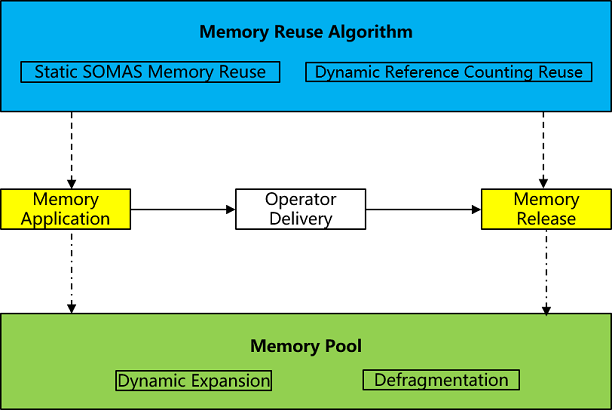
Device memory (hereinafter referred to as memory) is the most important resource in AI model training, and memory management is undoubtedly an extremely critical function in the runtime, with very high requirements on memory allocation and release performance as well as memory reuse efficiency. The memory management embodiment mainly focuses on memory allocation to the operator before the operator is issued, and memory release after the issuance for reuse by subsequent operators. The key function points are the memory pool and the memory reuse algorithm:
Memory pool serves as a base for memory management and can effectively avoid the overhead of frequent dynamic allocation of memory.
Memory reuse algorithm, as a core competency in memory management, needs to have efficient memory reuse results as well as minimal memory fragmentation.
Interfaces
The memory management-related interfaces are detailed in runtime interfaces, of which the two most important ones The two most important interfaces are the memory settings interface and the memory fragmentation management interface:
memory settings interface: mindspore.runtime.set_memory, setting the memory parameters to be managed using the memory pool and the memory reuse algorithm.
memory fragmentation management interface: environment variable MS_ALLOC_CONF. The behavior is determined by whether the hardware driver has the ability to map virtual memory to physical memory, if it does, it is turned on by default, otherwise it is turned off by default. This can be forced to be turned off by export MS_ALLOC_CONF=“enable_vmm:false”.
Memory Pool
The core idea of memory pool as a base for memory management is to pre-allocate a large block of contiguous memory, allocate it directly from the pool when applying for memory, and return it to the pool for reuse when releasing it, instead of frequently calling the memory application and release interfaces in the system, which reduces the overhead of frequent dynamic allocations, and improves system performance. MindSpore mainly uses the BestFit memory allocation algorithm, supports dynamic expansion of memory blocks and defragmentation, and sets the initialization parameters of the memory pool through the interface mindspore.runtime.set_memory(init_size,increase_size,max_size) to control the dynamic expansion size and maximum memory usage.
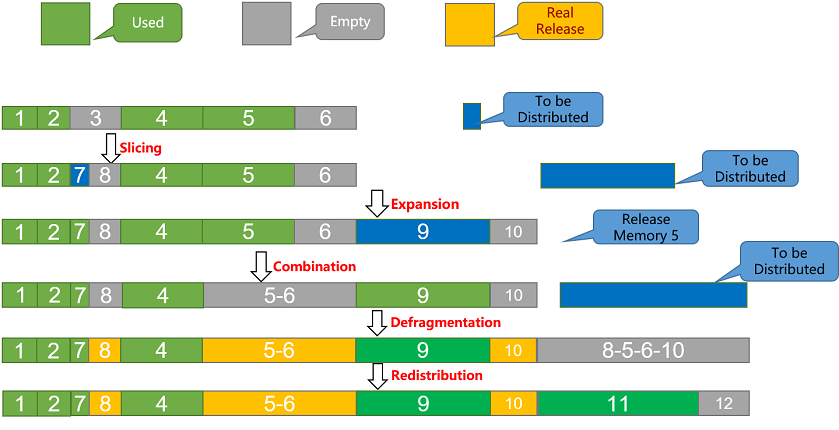
Slicing operation: When memory is allocated, free areas are sorted according to their sizes, the first free area that meets the requirements is found, allocated on demand, the excess is cut, and a new block of free memory is inserted.
Merge operation: When memory is reclaimed, neighboring free memory blocks are reclaimed and merged into one large free memory block.
Expansion operation: During memory allocation, when there is no free memory in the free area that meets the requirements, the memory pool is expanded by applying for a certain size of memory through the interface.
Fragmentation management: When memory is allocated, fragmentation management is triggered when a single free memory is not enough for allocation, but there is enough actual remaining memory to free up a block of free memory.
Memory Reuse Algorithm
Memory reuse algorithm serves as the core competitiveness of memory management, which can effectively reduce memory fragmentation through a good reuse algorithm. MindSpore implements two algorithms, static SOMAS reuse and dynamic reference counting reuse, each with its own advantages and disadvantages, and more scenarios are the combination of the two algorithms, which can be used according to the characteristics of the network structure as needed. Set the memory reuse algorithm through the interface mindspore.runtime.set_memory(optimize_level), O0 for dynamic memory reuse and O1 for static memory reuse.
Static Memory Reuse
Static memory reuse: the memory reuse relationship is mainly determined in the graph compilation phase. MindSpore implements the SOMAS (Safe Optimized Memory Allocation Solver ) algorithm, whose main idea is to perform aggregation analysis between the calculation graph parallel flow and data dependency, to get the inter-operator dependency, modeling the tensor global lifetime constraints through the dependencies, and solving the optimal memory static planning by using various heuristic algorithms to minimize the memory fragmentation and achieve memory reuse close to theoretical limits. The main steps are:
Model the graph.
Compute mutually exclusive constraint relationships between tensors based on modeling information.
Solved using a variety of heuristic algorithms.
Select the optimal solution result for memory allocation.
Pros: graph compilation phase statically plans memory reuse, can get global dependencies and minimize memory fragmentation.
Cons: The graph compilation phase fails to get the shape of the tensor in dynamic shape scenarios, making it unusable.
Dynamic Memory Reuse
Dynamic memory reuse is just the opposite of static memory reuse, transferring the memory reuse relationship to the execution phase, allocating memory completely dynamically during the execution process, applying for it as it comes, and ensuring that it is released when it is used up according to reference counting, to achieve the effect of dynamic reuse. The main steps are:
The number of users recorded for each tensor is called the reference count.
The reference count is decremented by 1 for each time the tensor is used during execution.
The reference count is reduced to 0, then the remaining memory is released to the memory pool.
Reset the initial reference count from step 1.
Pros: Dynamic memory reuse during the graph execution phase, fully generalized, especially friendly for dynamic shape and control flow scenarios.
Cons: The graph execution phase is reused on demand, obtains no global information, and is prone to memory fragmentation.